Plotting the results
in a 'power_curve' object, such as the
estimated power against sample size,
or the results of power4test_by_n()
or power4test_by_es().
Usage
# S3 method for class 'power_curve'
plot(
x,
what = c("ci", "power_curve"),
main = paste0("Power Curve ", "(Predictor: ", switch(x$predictor, n = "Sample Size", es
= "Effect Size"), ")"),
xlab = switch(x$predictor, n = "Sample Size", es = "Effect Size"),
ylab = "Estimated Power",
pars_ci = list(),
type = "l",
ylim = c(0, 1),
ci_level = 0.95,
...
)
# S3 method for class 'power4test_by_n'
plot(
x,
what = c("ci", "power_curve"),
main = "Estimated Power vs. Sample Size",
xlab = "Sample Size",
ylab = "Estimated Power",
pars_ci = list(),
type = "l",
ylim = c(0, 1),
ci_level = 0.95,
...
)
# S3 method for class 'power4test_by_es'
plot(
x,
what = c("ci", "power_curve"),
main = paste0("Estimated Power vs. Effect Size / Parameter (", attr(x[[1]],
"pop_es_name"), ")"),
xlab = paste0("Effect Size / Parameter (", attr(x[[1]], "pop_es_name"), ")"),
ylab = "Estiamted Power",
pars_ci = list(),
type = "l",
ylim = c(0, 1),
ci_level = 0.95,
...
)Arguments
- x
The object to be plotted. It can be a
power_curveobject, the output ofpower_curve(). It can also be the output ofpower4test_by_n()orpower4test_by_es().- what
A character vector of what to include in the plot. Possible values are
"ci"(confidence intervals for the estimated sample size) and"power_curve"(the crude power curve, if available). The default values depend on the type ofx.- main
The title of the plot.
- xlab, ylab
The labels for the horizontal and vertical axes, respectively.
- pars_ci
A named list of arguments to be passed to
arrows()to customize the drawing of the confidence intervals.- type
An argument of the default plot method
plot.default(). Default is"l". Seeplot.default()for other options.- ylim
A two-element numeric vector of the range of the vertical axis.
- ci_level
The level of confidence of the confidence intervals, if requested. Default is
.95, denoting 95%.- ...
Optional arguments. Passed to
plot()when drawing the base plot.
Details
The plot method of power_curve
objects currently plots the relation
between estimated power and
the predictor. Other elements
can be requested (see the argument
what), and they can be customized
individually.
Examples
# Specify the population model
model_simple_med <-
"
m ~ x
y ~ m + x
"
# Specify the effect sizes (population parameter values)
model_simple_med_es <-
"
y ~ m: l
m ~ x: m
y ~ x: s
"
# Simulate datasets to check the model
sim_only <- power4test(nrep = 10,
model = model_simple_med,
pop_es = model_simple_med_es,
n = 50,
fit_model_args = list(fit_function = "lm"),
do_the_test = FALSE,
iseed = 1234,
parallel = FALSE,
progress = FALSE)
# By n: Do a test for different sample sizes
# Set `parallel` to TRUE for faster, usually much faster, analysis
# Set `progress` to TRUE to display the progress of the analysis
out1 <- power4test_by_n(sim_only,
nrep = 10,
test_fun = test_parameters,
test_args = list(par = "y~x"),
n = c(25, 50, 100),
by_seed = 1234,
parallel = FALSE,
progress = FALSE)
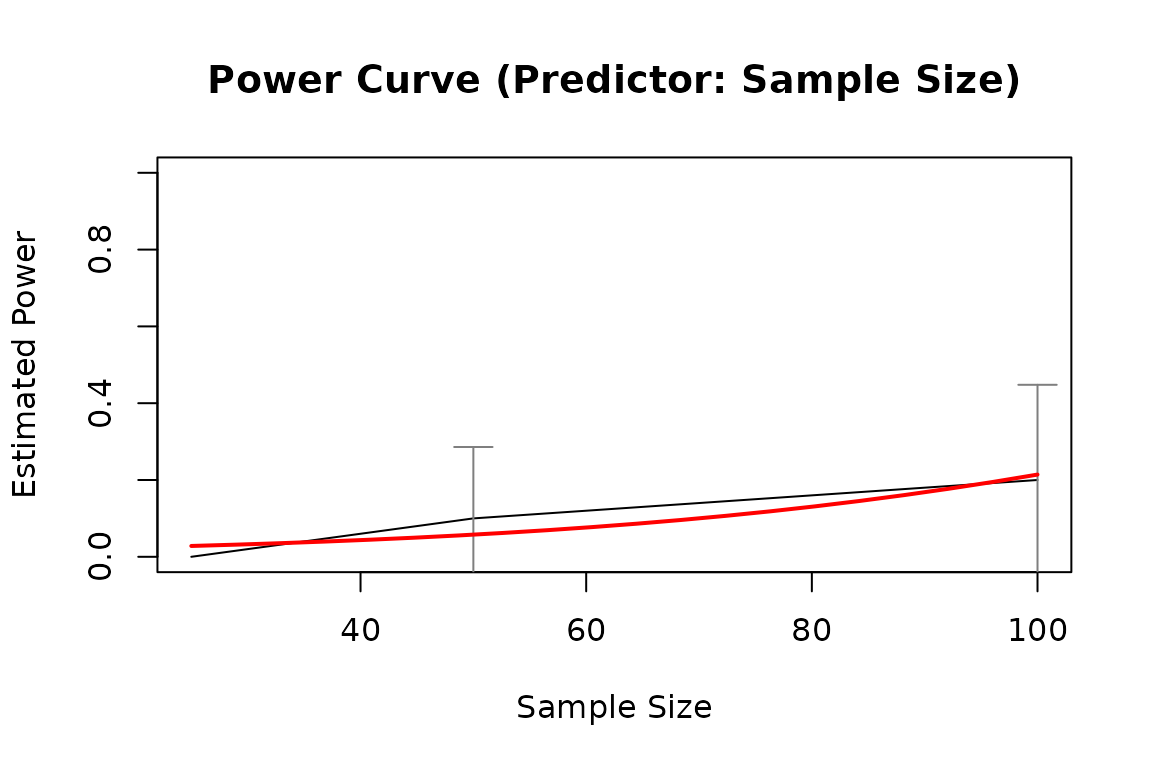
pout1 <- power_curve(out1)
pout1
#> Call:
#> power_curve(object = out1)
#>
#> Predictor: n (Sample Size)
#>
#> Model:
#>
#> Call: stats::glm(formula = reject ~ x, family = "binomial", data = reject1)
#>
#> Coefficients:
#> (Intercept) x
#> -4.28606 0.02986
#>
#> Degrees of Freedom: 29 Total (i.e. Null); 28 Residual
#> Null Deviance: 19.5
#> Residual Deviance: 17.37 AIC: 21.37
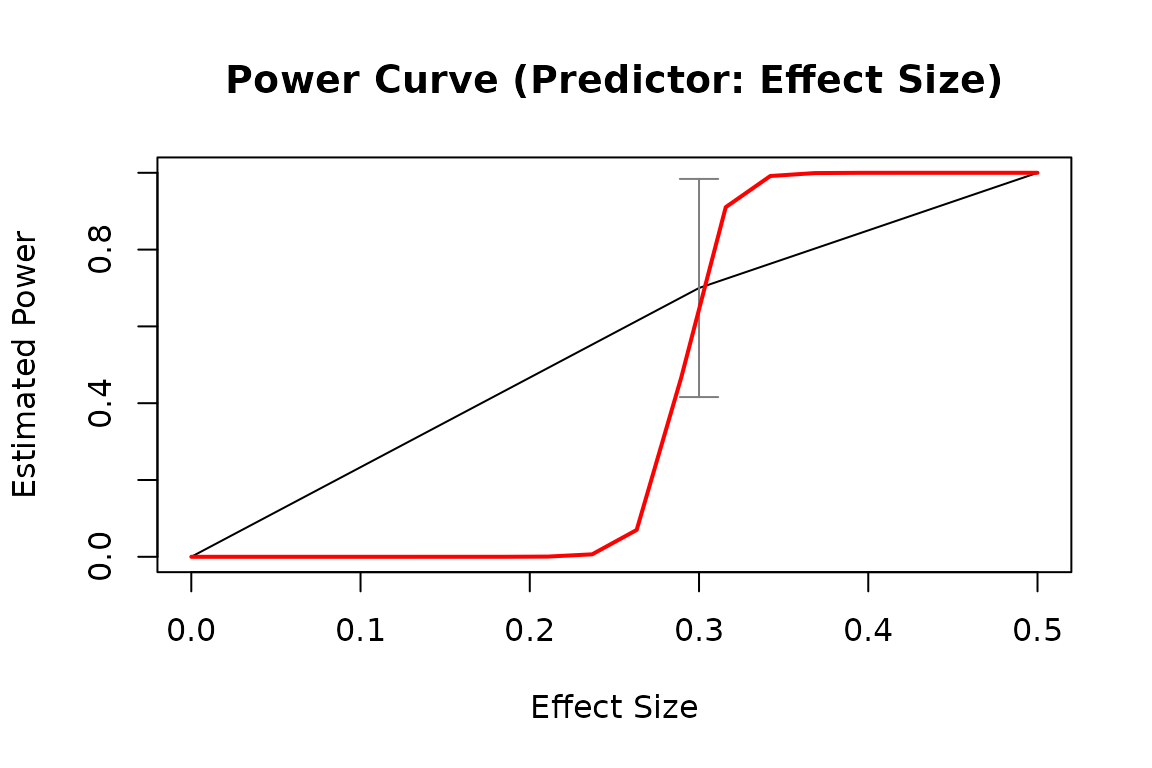
plot(pout1)
 # By pop_es: Do a test for different population values of a model parameter
# Set `parallel` to TRUE for faster, usually much faster, analysis
# Set `progress` to TRUE to display the progress of the analysis
out2 <- power4test_by_es(sim_only,
nrep = 10,
test_fun = test_parameters,
test_args = list(par = "y~x"),
pop_es_name = "y ~ x",
pop_es_values = c(0, .3, .5),
by_seed = 1234,
parallel = FALSE,
progress = FALSE)
pout2 <- power_curve(out2)
plot(pout2)
# By pop_es: Do a test for different population values of a model parameter
# Set `parallel` to TRUE for faster, usually much faster, analysis
# Set `progress` to TRUE to display the progress of the analysis
out2 <- power4test_by_es(sim_only,
nrep = 10,
test_fun = test_parameters,
test_args = list(par = "y~x"),
pop_es_name = "y ~ x",
pop_es_values = c(0, .3, .5),
by_seed = 1234,
parallel = FALSE,
progress = FALSE)
pout2 <- power_curve(out2)
plot(pout2)