Case Influence on Fit Measures (Approximate)
Source:R/fit_measures_change_approx.R
fit_measures_change_approx.RdGets a lavaan::lavaan() output and computes the
approximate change
in selected fit measures if a case is included.
Usage
fit_measures_change_approx(
fit,
fit_measures = c("chisq", "cfi", "rmsea", "tli"),
baseline_model = NULL,
case_id = NULL,
allow_inadmissible = FALSE,
skip_all_checks = FALSE
)Arguments
- fit
The output from
lavaan::lavaan()or its wrappers (e.g.,lavaan::cfa()andlavaan::sem()).- fit_measures
The argument
fit.measuresused in lavaan::fitMeasures. Default isc("chisq", "cfi", "rmsea", "tli"). Currently, the approximate method supports only these four measures.- baseline_model
The argument
baseline.modelused in lavaan::fitMeasures. Default isNULL.- case_id
If it is a character vector of length equals to the number of cases (the number of rows in the data in
fit), then it is the vector of case identification values. If it isNULL, the default, thencase.idxused bylavaanfunctions will be used as case identification values.- allow_inadmissible
If
TRUE, accepts a fit object with inadmissible results (i.e.,post.checkfromlavaan::lavInspect()isFALSE). Default isFALSE.- skip_all_checks
If
TRUE, skips all checks and allows users to run this function on any object oflavaanclass. For users to experiment this and other functions on models not officially supported. Default isFALSE.
Value
An fit_measures_change-class object, which is
matrix with the number of columns equals to the number of
requested fit measures, and the number of rows equals to the number
of cases. The row names are case identification values.
A print method is available for user-friendly output.
Details
For each case, fit_measures_change_approx() computes the
approximate differences in selected fit measures with and
without this case:
(Fit measure with all case) - (Fit measure without this case).
If the value of a case is positive, including the case increases an estimate.
If the value of a case is negative, including the case decreases an estimate.
Note that an increase is an improvement in fit for goodness of fit measures such as CFI and TLI, but a decrease is an improvement in fit for badness of fit measures such as RMSEA and model chi-square. This is a measure of the influence of a case on a fit measure if it is included.
The model is not refitted. Therefore, the result is only an
approximation of that of fit_measures_change(). However, this
approximation is useful for identifying potentially influential
cases when the sample size is very large or the model takes a long
time to fit. This function can be used to identify potentially
influential cases quickly and then select them to conduct the
leave-one-out sensitivity analysis using lavaan_rerun() and
fit_measures_change().
For the technical details, please refer to the vignette
on this approach: vignette("casewise_scores", package = "semfindr")
Supports both single-group and multiple-group models. (Support for multiple-group models available in 0.1.4.8 and later version).
Author
Idea by Mark Hok Chio Lai https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9196-7406, implemented by Shu Fai Cheung https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9871-9448.
Examples
library(lavaan)
# A path model
dat <- pa_dat
mod <-
"
m1 ~ a1 * iv1 + a2 * iv2
dv ~ b * m1
a1b := a1 * b
a2b := a2 * b
"
# Fit the model
fit <- lavaan::sem(mod, dat)
summary(fit)
#> lavaan 0.6-19 ended normally after 1 iteration
#>
#> Estimator ML
#> Optimization method NLMINB
#> Number of model parameters 5
#>
#> Number of observations 100
#>
#> Model Test User Model:
#>
#> Test statistic 6.711
#> Degrees of freedom 2
#> P-value (Chi-square) 0.035
#>
#> Parameter Estimates:
#>
#> Standard errors Standard
#> Information Expected
#> Information saturated (h1) model Structured
#>
#> Regressions:
#> Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
#> m1 ~
#> iv1 (a1) 0.215 0.106 2.036 0.042
#> iv2 (a2) 0.522 0.099 5.253 0.000
#> dv ~
#> m1 (b) 0.517 0.106 4.895 0.000
#>
#> Variances:
#> Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
#> .m1 0.903 0.128 7.071 0.000
#> .dv 1.321 0.187 7.071 0.000
#>
#> Defined Parameters:
#> Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
#> a1b 0.111 0.059 1.880 0.060
#> a2b 0.270 0.075 3.581 0.000
#>
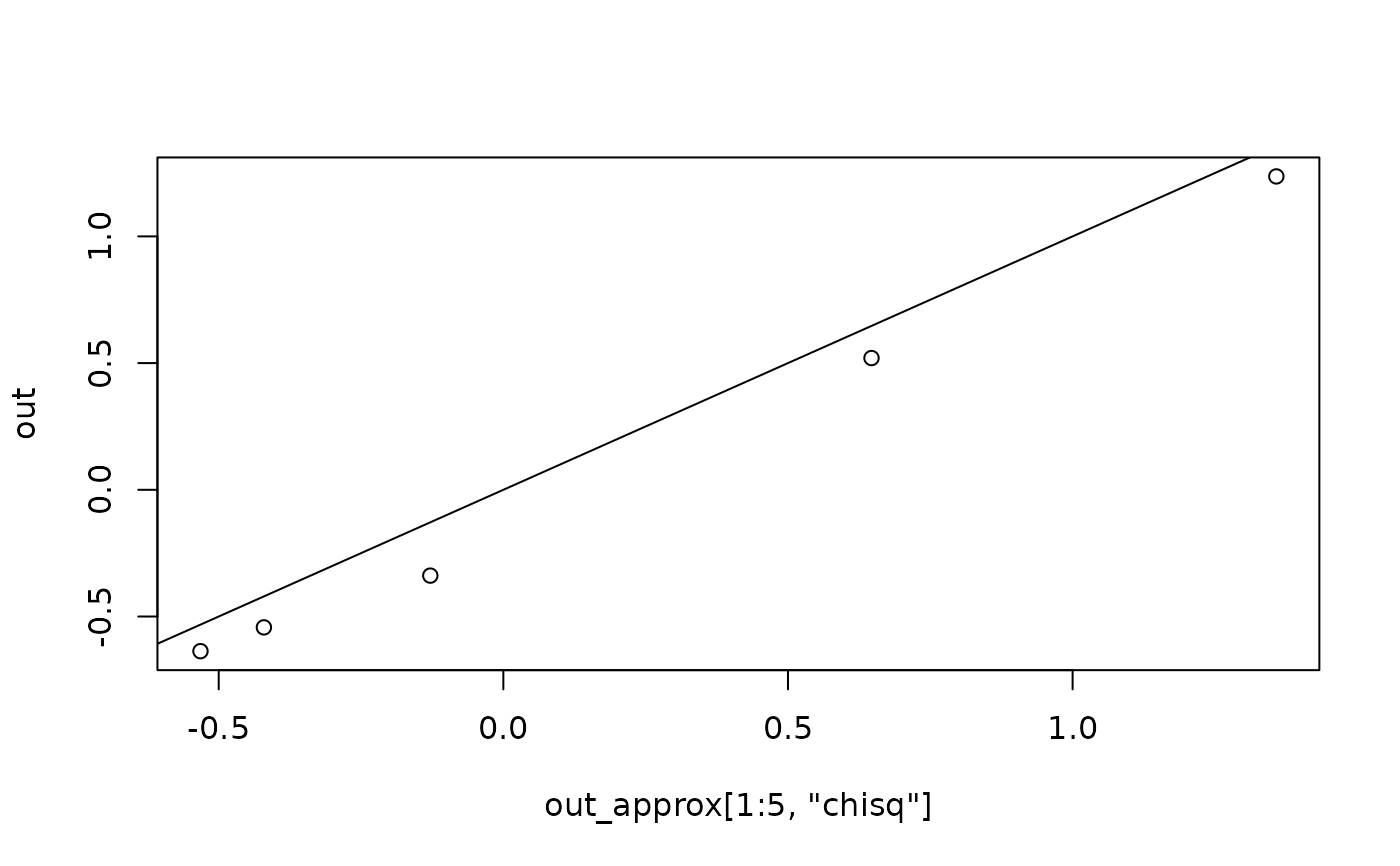
# Approximate changes
out_approx <- fit_measures_change_approx(fit, fit_measures = "chisq")
head(out_approx)
#> chisq
#> 1 0.15956516
#> 2 -0.01892880
#> 3 -0.38907022
#> 4 -0.15078126
#> 5 0.09685352
#> 6 0.11602751
# Fit the model several times. Each time with one case removed.
# For illustration, do this only for four selected cases
fit_rerun <- lavaan_rerun(fit, parallel = FALSE,
to_rerun = 1:5)
#> The expected CPU time is 0.22 second(s).
#> Could be faster if run in parallel.
# Compute the changes in chisq if a case is included
# vs. if this case is excluded.
# That is, case influence on model chi-squared.
out <- fit_measures_change(fit_rerun, fit_measures = "chisq")
# Case influence, for the first few cases
head(out)
#> chisq
#> 1 0.15407944
#> 2 -0.01944571
#> 3 -0.41673808
#> 4 -0.15430823
#> 5 0.09730667
# Compare the results
plot(out_approx[1:5, "chisq"], out)
abline(a = 0, b = 1)
 # A CFA model
dat <- cfa_dat
mod <-
"
f1 =~ x1 + x2 + x3
f2 =~ x4 + x5 + x6
f1 ~~ f2
"
# Fit the model
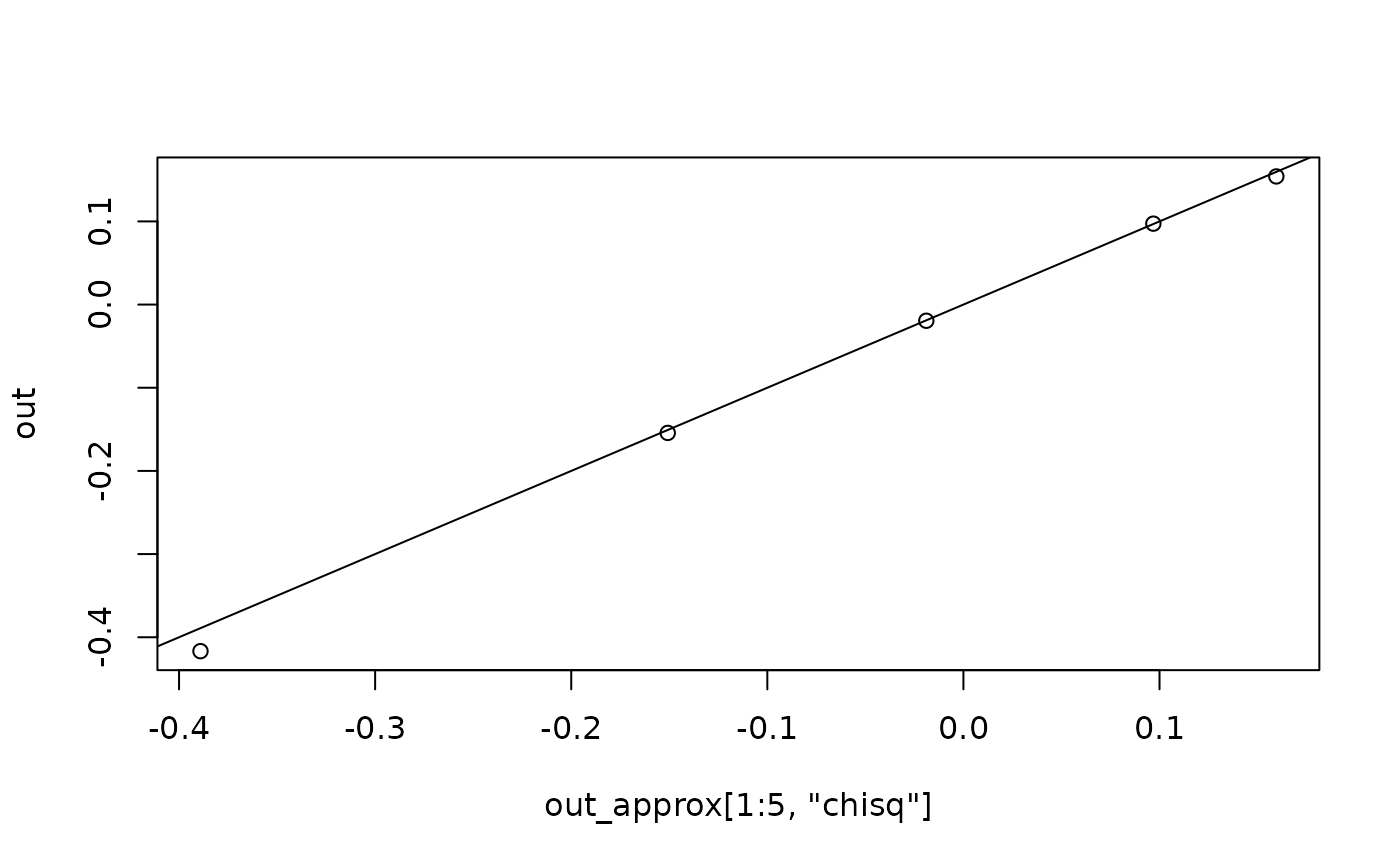
fit <- lavaan::cfa(mod, dat)
out_approx <- fit_measures_change_approx(fit, fit_measures = "chisq")
head(out_approx)
#> chisq
#> 1 -0.76276453
#> 2 0.99160651
#> 3 -0.13684245
#> 4 -0.02940289
#> 5 -0.54686780
#> 6 0.60740826
fit_rerun <- lavaan_rerun(fit, parallel = FALSE,
to_rerun = 1:5)
#> The expected CPU time is 0.31 second(s).
#> Could be faster if run in parallel.
# Compute the changes in chisq if a case is included
# vs. if this case is excluded.
# That is, case influence on fit measures.
out <- fit_measures_change(fit_rerun, fit_measures = "chisq")
# Results excluding a case, for the first few cases
head(out)
#> chisq
#> 1 -0.99210274
#> 2 0.90763725
#> 3 -0.25394609
#> 4 -0.03468346
#> 5 -0.63365168
# Compare the results
plot(out_approx[1:5, "chisq"], out)
abline(a = 0, b = 1)
# A CFA model
dat <- cfa_dat
mod <-
"
f1 =~ x1 + x2 + x3
f2 =~ x4 + x5 + x6
f1 ~~ f2
"
# Fit the model
fit <- lavaan::cfa(mod, dat)
out_approx <- fit_measures_change_approx(fit, fit_measures = "chisq")
head(out_approx)
#> chisq
#> 1 -0.76276453
#> 2 0.99160651
#> 3 -0.13684245
#> 4 -0.02940289
#> 5 -0.54686780
#> 6 0.60740826
fit_rerun <- lavaan_rerun(fit, parallel = FALSE,
to_rerun = 1:5)
#> The expected CPU time is 0.31 second(s).
#> Could be faster if run in parallel.
# Compute the changes in chisq if a case is included
# vs. if this case is excluded.
# That is, case influence on fit measures.
out <- fit_measures_change(fit_rerun, fit_measures = "chisq")
# Results excluding a case, for the first few cases
head(out)
#> chisq
#> 1 -0.99210274
#> 2 0.90763725
#> 3 -0.25394609
#> 4 -0.03468346
#> 5 -0.63365168
# Compare the results
plot(out_approx[1:5, "chisq"], out)
abline(a = 0, b = 1)
 # A latent variable model
dat <- sem_dat
mod <-
"
f1 =~ x1 + x2 + x3
f2 =~ x4 + x5 + x6
f3 =~ x7 + x8 + x9
f2 ~ a * f1
f3 ~ b * f2
ab := a * b
"
# Fit the model
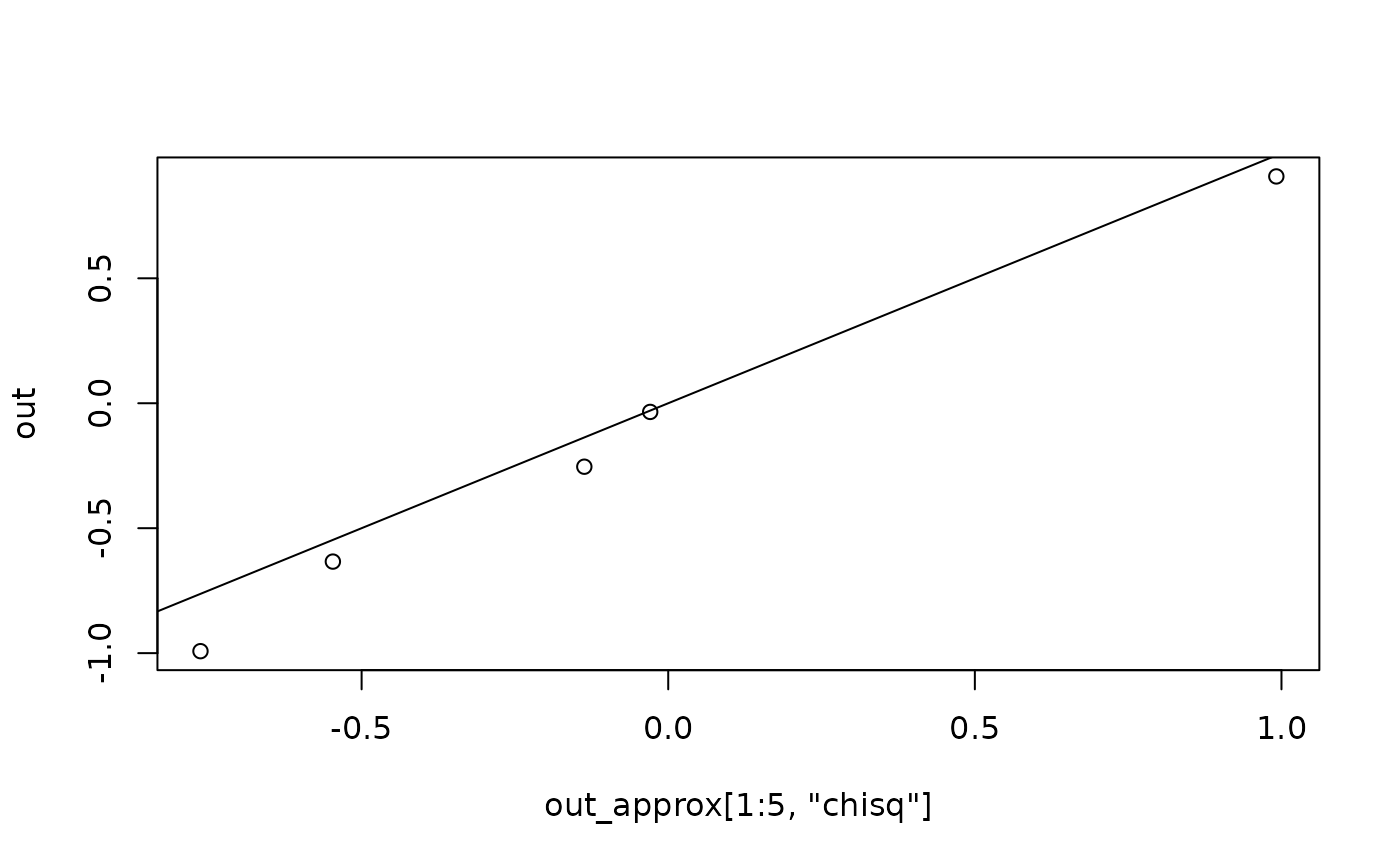
fit <- lavaan::sem(mod, dat)
out_approx <- fit_measures_change_approx(fit, fit_measures = "chisq")
head(out_approx)
#> chisq
#> 1 -0.1283103
#> 2 -0.5320442
#> 3 0.6467449
#> 4 1.3578723
#> 5 -0.4206413
#> 6 0.2202259
fit_rerun <- lavaan_rerun(fit, parallel = FALSE,
to_rerun = 1:5)
#> The expected CPU time is 0.32 second(s).
#> Could be faster if run in parallel.
# Compute the changes in chisq if a case is excluded
# vs. if this case is included.
# That is, case influence on model chi-squared.
out <- fit_measures_change(fit_rerun, fit_measures = "chisq")
# Case influence, for the first few cases
head(out)
#> chisq
#> 1 -0.3385932
#> 2 -0.6367473
#> 3 0.5199304
#> 4 1.2366084
#> 5 -0.5428558
# Compare the results
plot(out_approx[1:5, "chisq"], out)
abline(a = 0, b = 1)
# A latent variable model
dat <- sem_dat
mod <-
"
f1 =~ x1 + x2 + x3
f2 =~ x4 + x5 + x6
f3 =~ x7 + x8 + x9
f2 ~ a * f1
f3 ~ b * f2
ab := a * b
"
# Fit the model
fit <- lavaan::sem(mod, dat)
out_approx <- fit_measures_change_approx(fit, fit_measures = "chisq")
head(out_approx)
#> chisq
#> 1 -0.1283103
#> 2 -0.5320442
#> 3 0.6467449
#> 4 1.3578723
#> 5 -0.4206413
#> 6 0.2202259
fit_rerun <- lavaan_rerun(fit, parallel = FALSE,
to_rerun = 1:5)
#> The expected CPU time is 0.32 second(s).
#> Could be faster if run in parallel.
# Compute the changes in chisq if a case is excluded
# vs. if this case is included.
# That is, case influence on model chi-squared.
out <- fit_measures_change(fit_rerun, fit_measures = "chisq")
# Case influence, for the first few cases
head(out)
#> chisq
#> 1 -0.3385932
#> 2 -0.6367473
#> 3 0.5199304
#> 4 1.2366084
#> 5 -0.5428558
# Compare the results
plot(out_approx[1:5, "chisq"], out)
abline(a = 0, b = 1)