Get Started
semdplot.Rmd(Work-In-Progress)
Load the Package and Fit a Path Model
library(semdplot)
# A sample dataset from semdplot
dat <- data_pa
library(lavaan)
#> This is lavaan 0.6-15
#> lavaan is FREE software! Please report any bugs.
mod <-
"
m11 ~ a11*x1 + a21*x2 + c1 + c2
m12 ~ b12*m11 + c1 + c2
m21 ~ a12*x1 + a22*x2 + c1 + c2
m22 ~ b22*m21 + c1 + c2
y1 ~ b12y1*m12 + c1 + c2
y2 ~ b22y2*m22 + c1 + c2
ind_1 := a11*b12*b12y1
ind_2 := a21*b22*b22y2
"
fit <- sem(mod, dat)
summary(fit, fit.measures = TRUE)
#> lavaan 0.6.15 ended normally after 7 iterations
#>
#> Estimator ML
#> Optimization method NLMINB
#> Number of model parameters 27
#>
#> Number of observations 200
#>
#> Model Test User Model:
#>
#> Test statistic 76.709
#> Degrees of freedom 18
#> P-value (Chi-square) 0.000
#>
#> Model Test Baseline Model:
#>
#> Test statistic 377.440
#> Degrees of freedom 39
#> P-value 0.000
#>
#> User Model versus Baseline Model:
#>
#> Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 0.827
#> Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 0.624
#>
#> Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
#>
#> Loglikelihood user model (H0) -1709.158
#> Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -1670.803
#>
#> Akaike (AIC) 3472.315
#> Bayesian (BIC) 3561.370
#> Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (SABIC) 3475.831
#>
#> Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
#>
#> RMSEA 0.128
#> 90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.099
#> 90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.158
#> P-value H_0: RMSEA <= 0.050 0.000
#> P-value H_0: RMSEA >= 0.080 0.996
#>
#> Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
#>
#> SRMR 0.090
#>
#> Parameter Estimates:
#>
#> Standard errors Standard
#> Information Expected
#> Information saturated (h1) model Structured
#>
#> Regressions:
#> Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
#> m11 ~
#> x1 (a11) 0.543 0.066 8.202 0.000
#> x2 (a21) 0.572 0.069 8.345 0.000
#> c1 0.258 0.070 3.701 0.000
#> c2 0.460 0.074 6.213 0.000
#> m12 ~
#> m11 (b12) 0.290 0.055 5.246 0.000
#> c1 0.165 0.073 2.269 0.023
#> c2 0.185 0.079 2.322 0.020
#> m21 ~
#> x1 (a12) -0.068 0.066 -1.027 0.304
#> x2 (a22) 0.184 0.069 2.678 0.007
#> c1 -0.011 0.070 -0.158 0.874
#> c2 -0.138 0.074 -1.861 0.063
#> m22 ~
#> m21 (b22) 0.249 0.076 3.274 0.001
#> c1 0.031 0.076 0.405 0.685
#> c2 -0.023 0.082 -0.280 0.780
#> y1 ~
#> m12 (b121) 0.442 0.070 6.267 0.000
#> c1 -0.041 0.078 -0.525 0.599
#> c2 -0.053 0.084 -0.636 0.525
#> y2 ~
#> m22 (b222) 0.511 0.065 7.822 0.000
#> c1 0.210 0.072 2.895 0.004
#> c2 -0.027 0.077 -0.350 0.727
#>
#> Covariances:
#> Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
#> .y1 ~~
#> .y2 0.028 0.075 0.377 0.706
#>
#> Variances:
#> Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
#> .m11 0.928 0.093 10.000 0.000
#> .m12 0.987 0.099 10.000 0.000
#> .m21 0.930 0.093 10.000 0.000
#> .m22 1.118 0.112 10.000 0.000
#> .y1 1.115 0.112 10.000 0.000
#> .y2 1.005 0.101 10.000 0.000
#>
#> Defined Parameters:
#> Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
#> ind_1 0.070 0.019 3.612 0.000
#> ind_2 0.073 0.026 2.840 0.005Compute Residuals for the PLots
The function casewise_residuals() can be used to compute
the necessary residuals (please refer to
vignettes("casewise_residuals") on the computation):
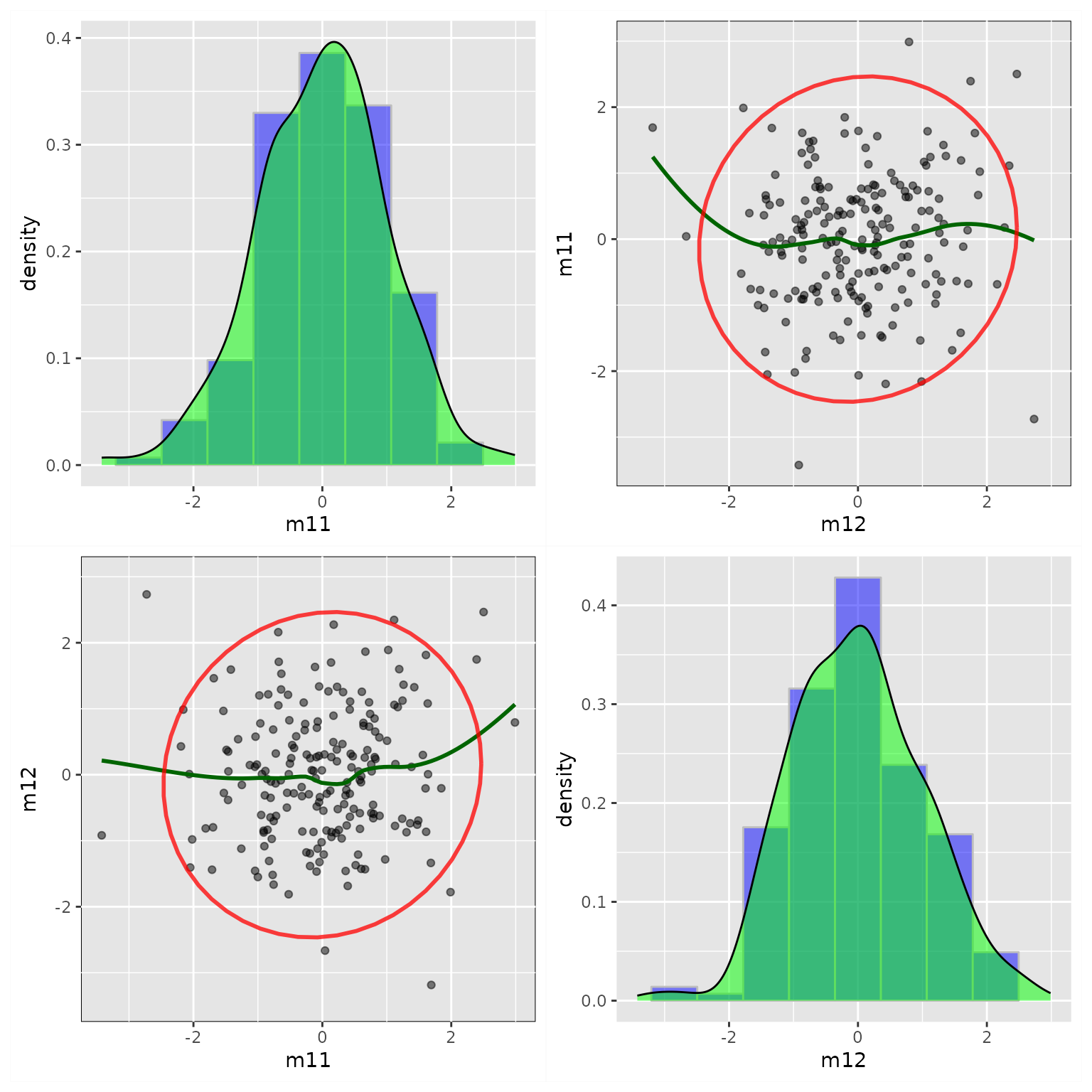
fit_res <- casewise_residuals(fit)Plot Partial Plots and Residual Plots for Selected Variables
The output of casewise_residuals() has a
plot() method. Simply use plot() can produce
the plots. If necessary, users can use x_names and
y_names to set the \(x\)
and \(y\) variables to be included:
p <- plot(fit_res,
x_names = c("x1", "x2", "m11", "m12", "m21"),
y_names = c("m11", "m12", "m21", "m22", "y1", "y2"))
plot(p)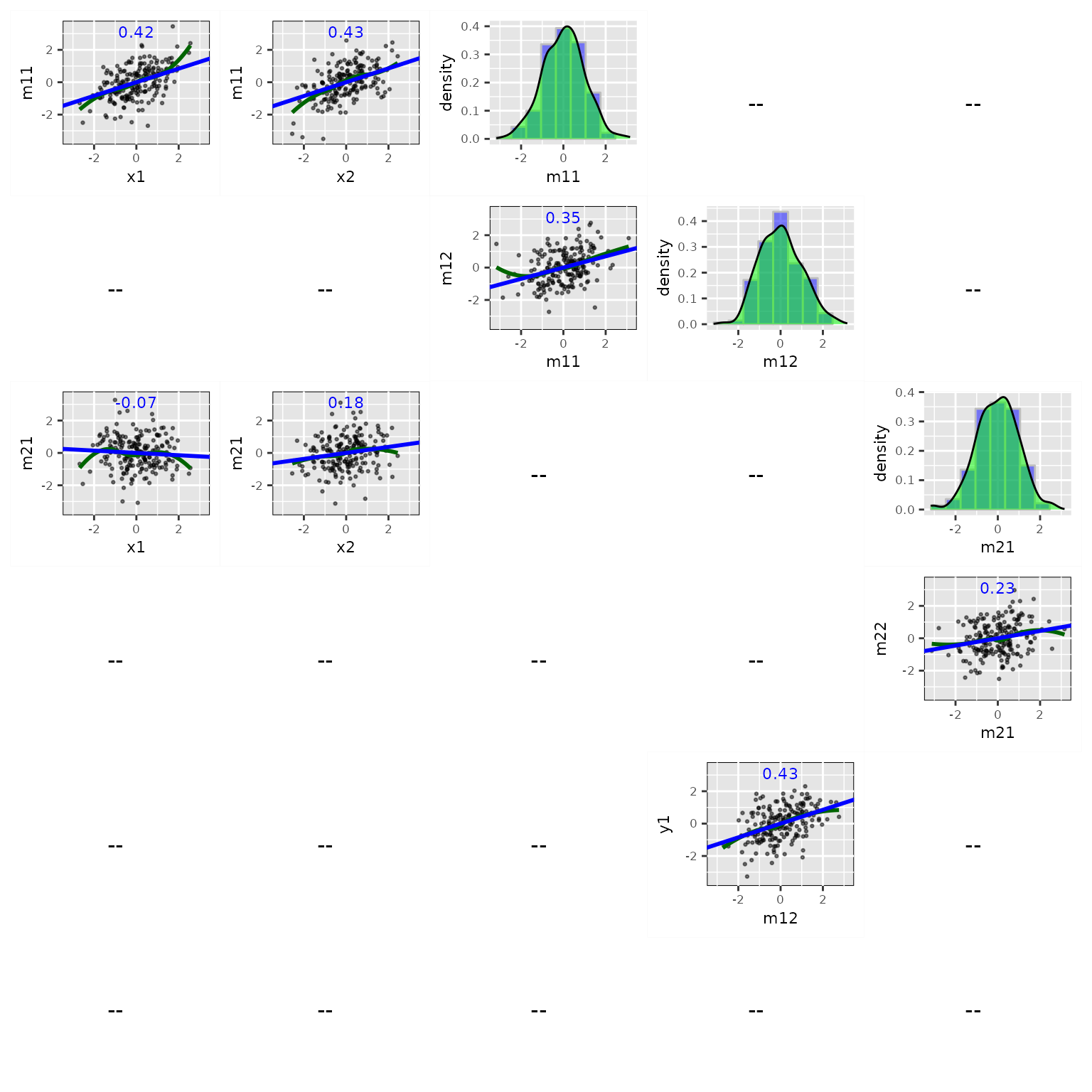
The output is a ggplot2 plot. It can be customized.
Please refer to plot.semdplot_residuals() on the
options.
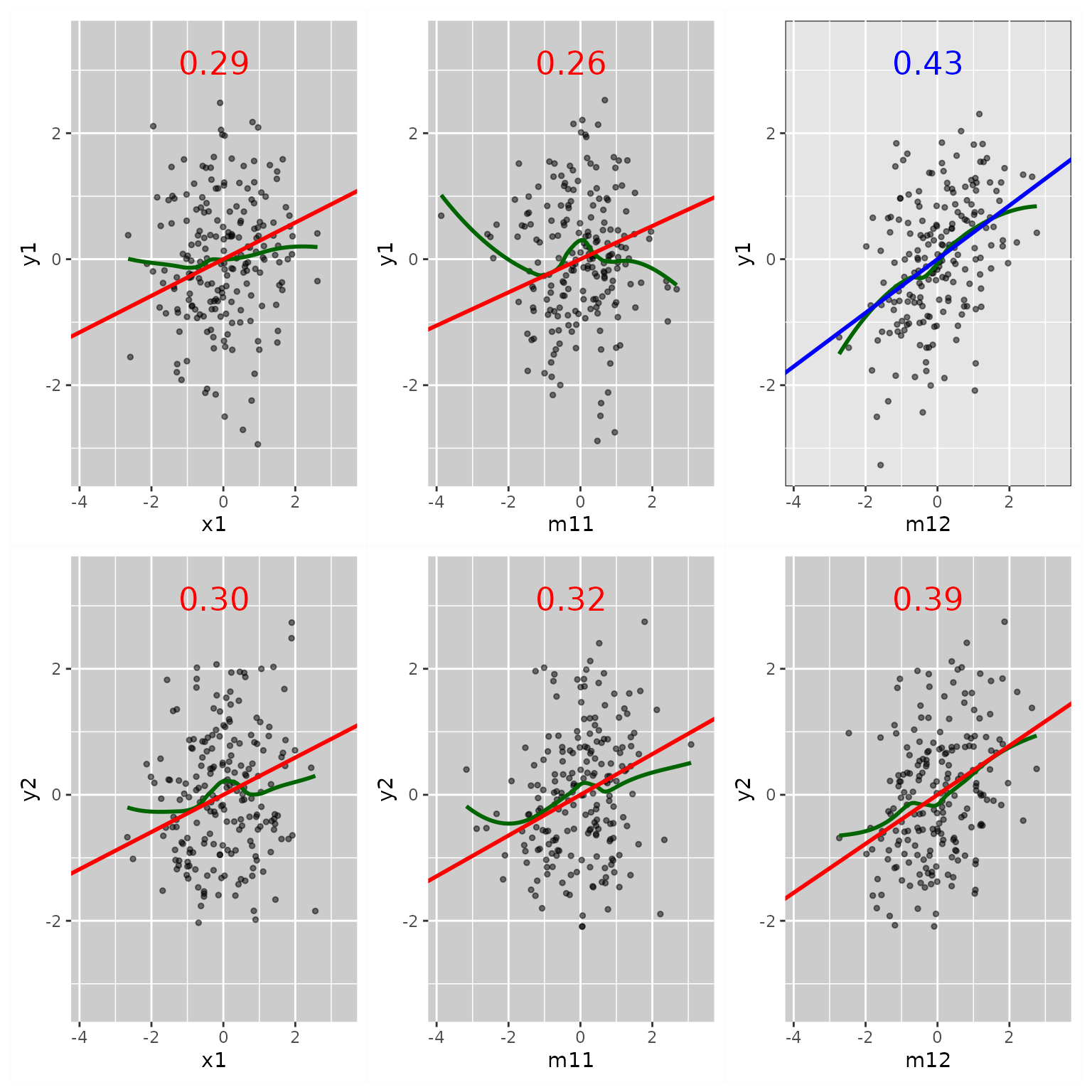
If A Path Does Not Exist, Add It
For paths not in the model but could have been added, residuals can
be computed by fitting a model with this path added. This is done when
calling casewise_residuals() and set add_path
to `TRUE:
fit_res_add <- casewise_residuals(fit, add_path = TRUE)If these residuals are computed, they will be plotted by
plot.semdplot_residuals():
p2 <- plot(fit_res_add,
x_names = c("x1", "x2", "m11", "m12", "m21"),
y_names = c("m11", "m12", "m21", "m22", "y1", "y2"))
plot(p2)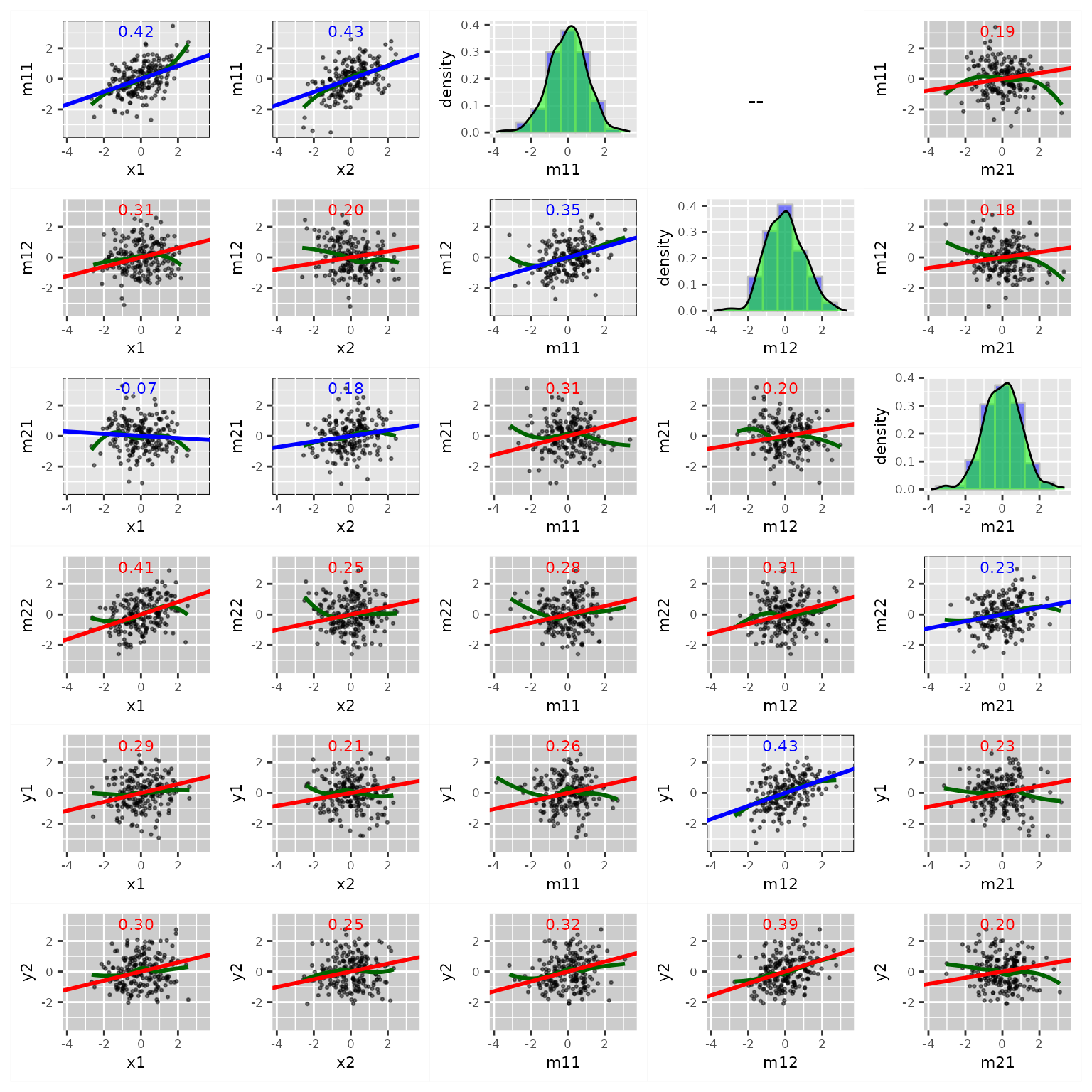
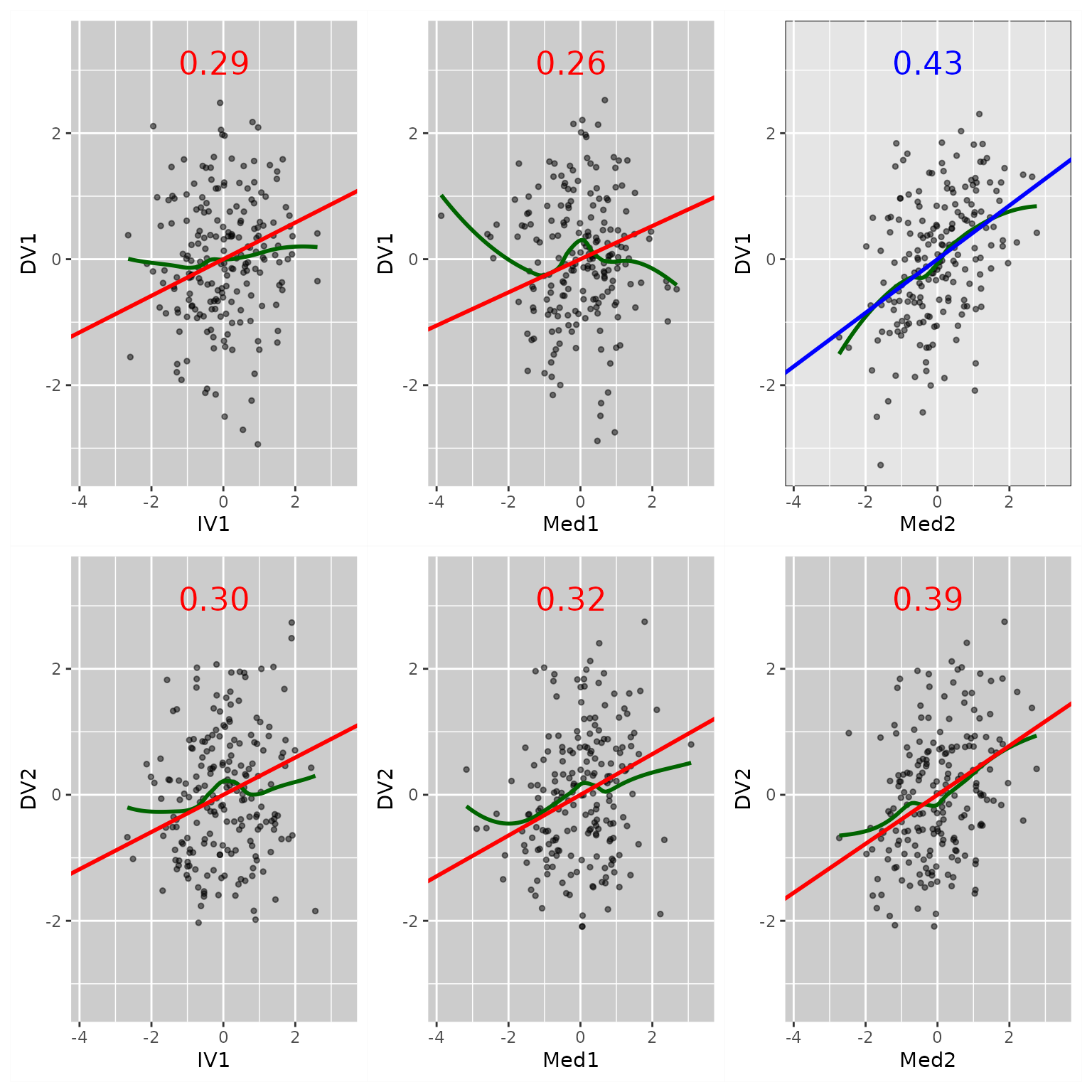
Plot Only One Partial Plot
This example also illustrates how to change the style.
Note that, if ggplot2 functions are used when changing
the aesthetics, users need to load ggplot2 first, e.g.,
rel().
library(ggplot2)
p2 <- plot(fit_res_add,
x_names = "x1",
y_names = "m11",
partial_point_aes = list(size = 4,
color = "blue"),
partial_reg_aes = list(size = 10),
partial_loess_aes = list(color = "black",
linetype = "dashed"),
partial_b_aes = list(size = rel(10)))
plot(p2)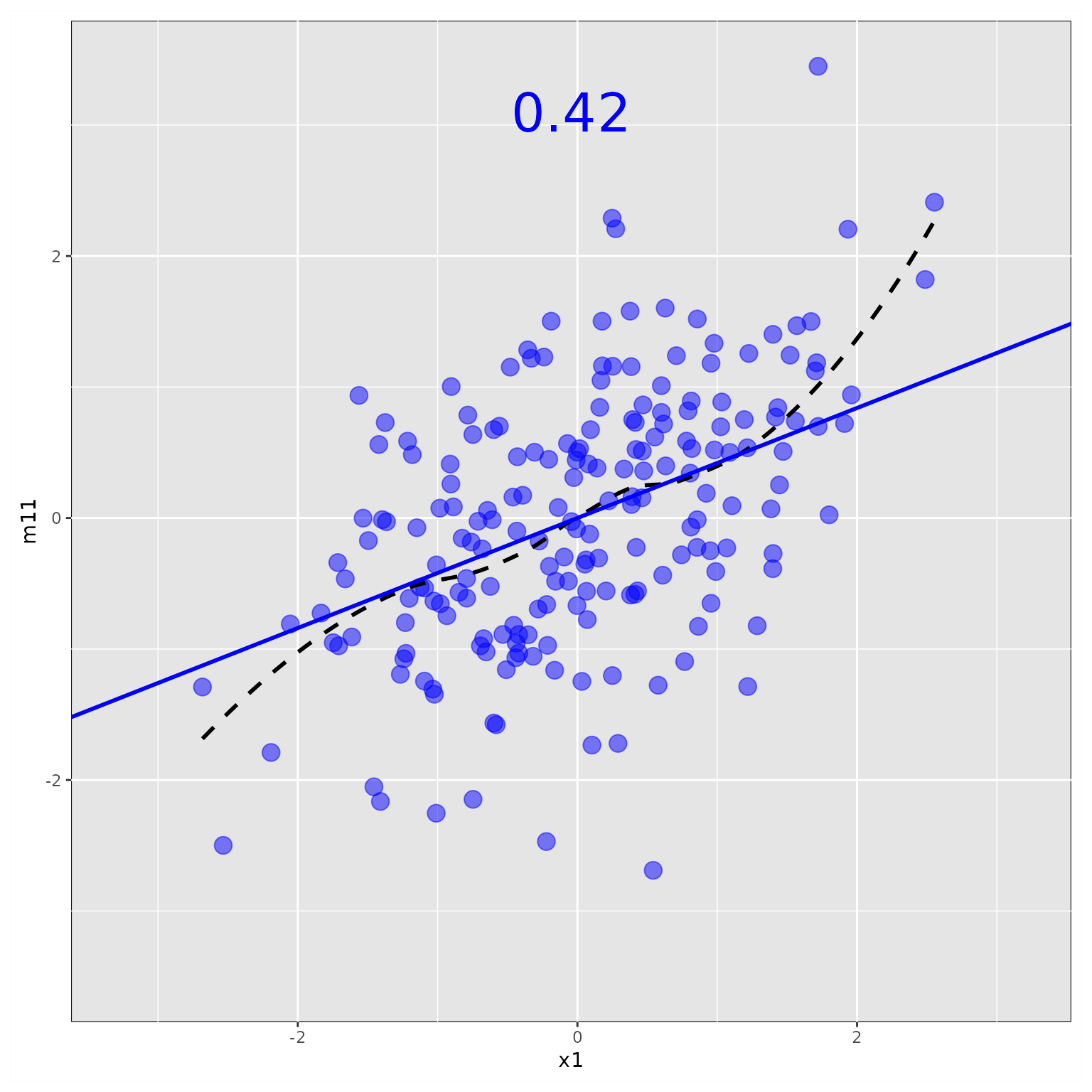
Plot of Residuals only
By setting what = "residual", the plot()
method can produce only plots for residuals of endogenous variables:
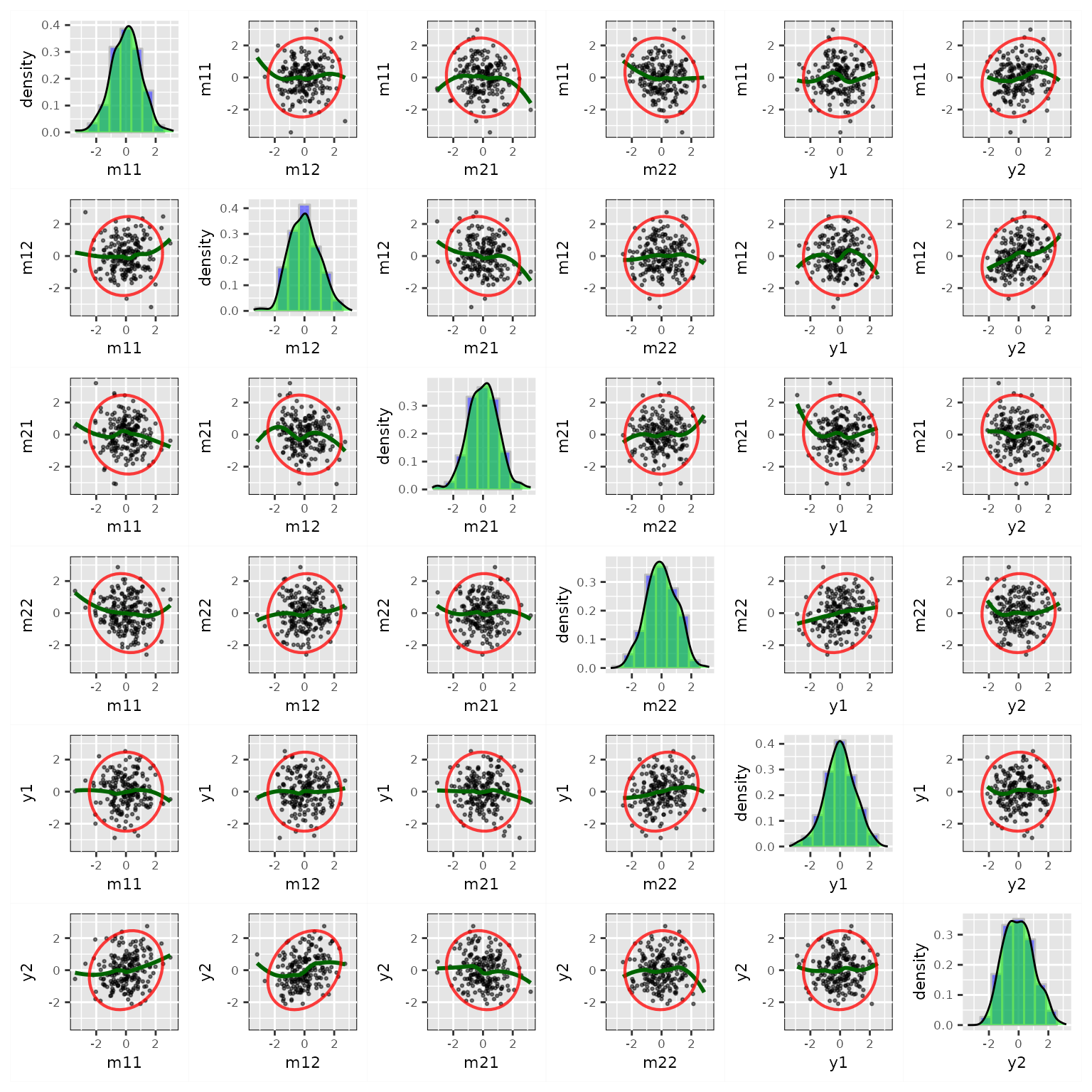
Users can also use y_names to select only some of the
endogenous variables for the plot: